30 Mars 2016
The emergence of Data Centers and Storage Area Networks --other computing applications drives the needs for ultra-high speed data interconnections and structured cabling. The interconnect media choices include wireless technology, copper cable and optical fiber cable. Fiber cable offers bandwidth and supports The Highest The Highest data rates. There are single mode and multimode fiber type. Different kinds of fiber optic transceivers connect with fiber resulting and in different performances and costs. So it's significant for the network designers to Understand the fiber type and select the right fiber optic transceivers and Corresponding fiber for network interconnection.
There are three main kinds of optical fiber suitable for network interconnection use:
9 / 125μm Single-mode fiber 50 / 125μm multimode fiber 62.5 / 125μm multimode fiber
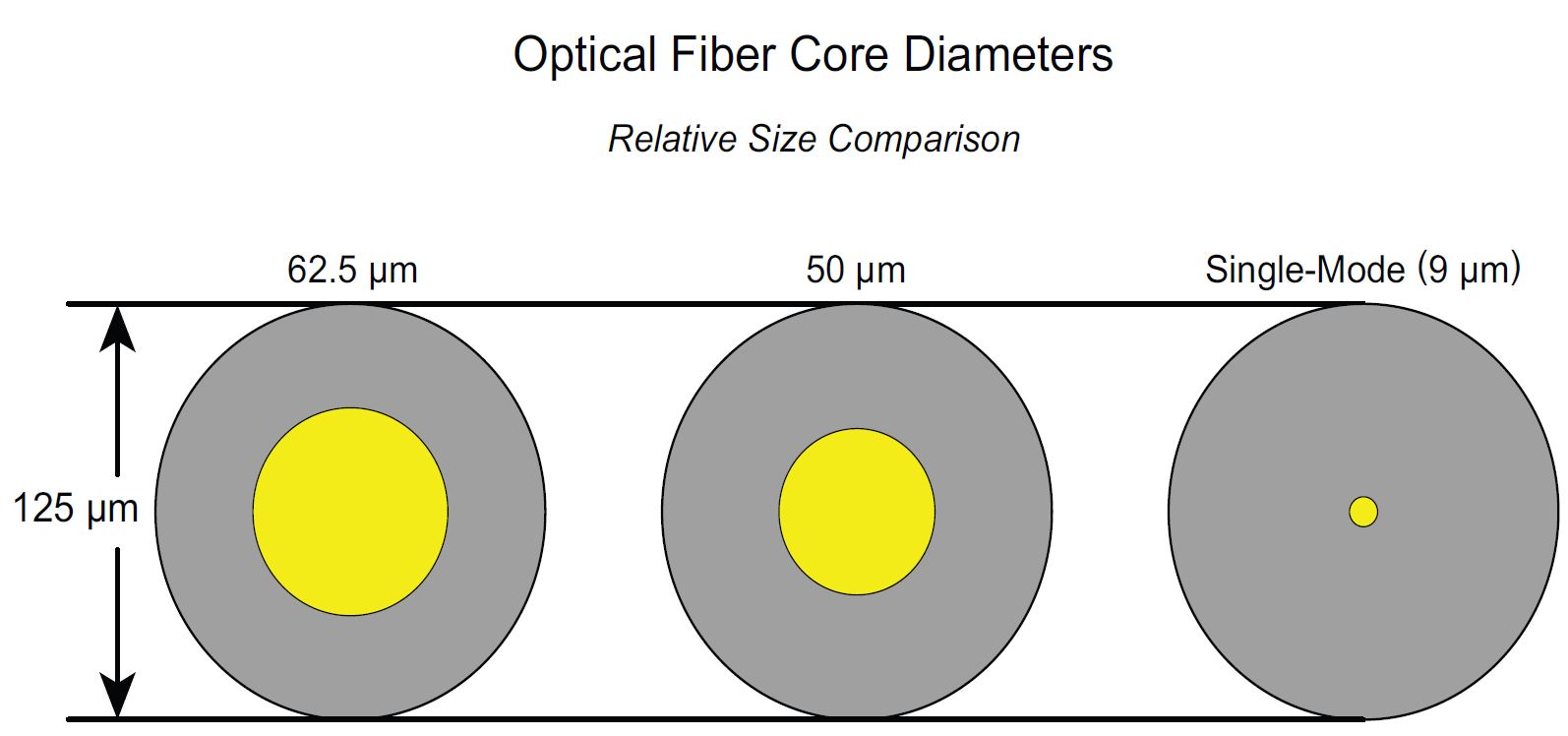
The Above numbers respectivement mean the diameter of the core glass Where the light travels outside and glass cladding diameter qui est la même Almost to the MOST fiber type. So the difference of Each fiber types is Caused by the core diameter. It has great impact on system performance and system cost contre When balanced network implementation needs. Two primary affected are factoring attenuation and bandwidth.
Attenuation is the reduction of signal power, or loss, as light travels through an optical fiber. Fiber attenuation is Measured in decibels per kilometer (dB / km). The Higher the attenuation, The Higher rate of signal loss of a fiber length Given. Single-mode fiber Generally operate at 1310nm (for short range) while multimode fibers operate at 850 nm or 1300 nm. Attenuation is not usually regarded to be the main limiting factor in shorts rank transmissions. Aim it can because big differences in high speed network Such As 100Gb / s.
Bandwidth means clustering the carrying capacity of fiber. For single mode fiber, the modal dispersion can be ignored since icts small core diameter. Bandwidth behavior of multimode fiber is Caused by multimodal dispersion During the light traveling along different paths in the core of the fiber. It has an impact on the system performance and data rate handling. Multimode fiber uses a graded index profile to minimize modal dispersion. This design maximizes bandwidth while Maintaining larger core diameters for simplified assembly, connectivity and low cost. So manufacturers start to Develop higher-performance multimode fiber systems with Higher bandwidth.
A fiber optic transceiver Consists usually the optical light sources Typically LED-light emitting diode and optical receivers. Since the core diameter size and primary operating Wavelengths of single mode fiber and multimode fiber are different, the associated transceiver technology and connectivity aussi will be different. So is the system cost.
To please use the single mode fibers Generally for long distance applications (multi-kilometer reach), transceivers with lasers Such As SFPP-10GE-LR (an SFP + 1310nm 10 km Transceiver Supporting single mode fiber) That operate at along Wavelengths with smaller spot -size and narrower spectral width. Purpose thesis kinds of transceivers need Higher precision alignment and connector Tighter tolerance to smaller core diameters. THUS, it causes Higher costs for single mode fiber interconnections. To lower the cost, manufacturers Produce transceivers based on VCSEL (vertical cavity emitting laser area), for example, 10G-SR-SFPP (an SFP + Transceiver Supporting 850nm 300m multimode fiber), qui are optimized for use with multimode fiber. Transceivers Applying low cost VCSEL technology to Develop for 50 / 125μm multimode fiber, take advantage of the larger core diameter to gain high coupling efficiency and 'wider geometrical tolerances. OM3 and OM4 multimode fibers offer high bandwidth to carrier data rates from 10Mb / s to 100Gb / s.
Optical fiber is an easily-installed medium That Is immune to electromagnetic interface and est more efficient in terms of power consumption. What's more, fiber optic cable can save space and cost with Higher density cabling and the port density over copper cabling. For single mode fiber and multimode fiber contents, each one Has Its Advantages and disadvantages. Network designers shoulds better select the right type of fiber optic transceivers and related fiber selon specific situations for Higher system performance. Of course, cost is substantial Reviews another factor to be regarded.
Originally published at www.fiber-optic-equipment.com